Your Custom Text Here
Beyond the hype on terra.money
Key Takeaways
There is a hidden negative multiplier effect in the Terra system, that will dampen the price of Luna - until a network effect is reached.
There is a hidden viral loop in the Token economics, that incentivizes merchants to also be stakers and enlist as many other merchants as possible to drive their unit costs down.
The interplay of the two loops optimizes for long-term oriented actors to populate the consensus layer, a net positive.
Both the decision to start with Korea, and the go-to-market strategy Terra is deploying, are moats in the making, if executed well.
Luna lost ~75% of its value since listing in Q3 2019. At current prices, pre-sale investors are likely at break-even, having already booked (some) profit.
Conservative estimates from a DCF model, show that Luna, at current price levels, is undervalued by between 38% and 67%.
Terra.money; seigniorage shares done right
Terra is a stablecoin project out of Korea that deploys a seigniorage shares model in order to algorithmically ensure stability in the system. This is not the first time we see an asset of this type hit the market - Basis and The Reserve are the two most prominent ones that jump to mind. However, where its predecessors have thus far failed, Terra is getting promising traction.
Terra's base layer token economics
Terra is essentially composed of 2 tokens that live in parallel; Terra and Luna. Terra(X) is the stablecoin component - where (X) is any fiat equivalence supported on Terra (e.g X = KRW, USD etc), and Luna is the protocol token. Terra powers the user facing part of the terra.money platform, while Luna - a fixed supply variable price token - powers the infrastructure.
The blockchain layer in Terra collapses the multiple layers of payments processors present in modern day e-commerce and P2P payments value chains, and manages to reduce the cost of executing transactions by as much as 80% - ledger fees start a default of 0.1% and are capped at 1%. Validators have to stake Luna in order to be granted the right to validate blocks and access a perpetual stream of ledger fees as a reward for their work - and equivalently are exposed to slashing if they are found to misreport ledger state. A validator's Luna stake represents pro-rata odds of generating Terra blocks; i.e. the more Luna you stake, the higher the expected value of the rewards you claim. Luna holders are also granted governance rights over the fiscal stimulus treasury - endowments to dApps that apply to the Terra ecosystem.
How Terra maintains stability
Terra maintains stability by algorithmically adjusting the money supply. In an excess demand condition, where Terra would go off its peg on the upside, the system mints more Terra and burns an equivalent (according to the spot exchange rate) amount of Luna. Conversely, when Terra is experiencing a lot of selling pressure, the system mints and auctions more Luna in order to buy back and burn Terra - contracting the money supply and diluting Luna holders.
A hidden negative multiplier effect in the stability mechanism
Herein lies the first issue with Terra's model; validator dilution. Until the stablecoin instrument has enough brand recognition, trust and ultimately network effect, so that the perceived risk of holding Terra on balance sheet is low, merchant incentives remain somewhat warped. Here's what I mean:
1 unit of TerraUSD on balance sheet is worth less than 1 unit of fiat USD, due to their differing counterparty risk profiles.
The former is backed by a consortium of private actors, while the latter is backed by the US government. Until a network effect enough strong enough to persuade merchants otherwise is in place, they are incentivised to offload that balance sheet risk and head for the nearest exit to government backed fiat.
The effect is continued dilution for Luna holders.
Similarly, in the pegging process described earlier - where equivalent values of Terra and Luna are arbitraged away to bring the peg to balance, in order for the arbitrageur to book profit, they need to immediately liquidate the Luna they receive in equivalence. If that incentive structure holds, then not only are validators diluted by inflation in the short term, but the value of their Luna holdings reduces further as market makers immediately offload the minted Luna to market, increasing the available supply of the asset. Absent a network effect, this dynamic acts as a negative (unintended) multiplier in the Terra system.
Compensating validators for dilution
To incentivise validators to weather the storm, Terra introduces long-term validator incentives in the form of inflationary rewards (currently ~10%). Effectively Terra is inviting potential validators to ride out the J-curve with them and collect beans in the process. At a high-level, the idea makes sense; the negative multiplier effect should hold only until the network effect is reached. Once that is achieved, then the loop should turn from adverse to virtuous, and value would start to trickle back into Luna tokens.
A hidden viral loop in the token economics
Things get interesting when the boundaries between merchant/user of the Terra blockchain and validator start to blur. There is no provision in the model to explicitly prohibit merchants from also become holders of Luna and validators in Terra's consensus. In fact, it seems that Terra implicitly optimizes for that. Of course, not all merchants will wear investor hats, but potentially the more savvy (and dare I say the more influential) will recognise that since they are already long the platform as early adopters, they can leverage up on the upside by staking Luna, while reducing their unit costs and hedging the downside, by collecting ledger fees.
Now were that the case, merchant validators are even more incentivized to evangelize Terra; the more merchants on the platform, the more ledger fees they would collect, the more their unit economics would improve and the quicker the platform would get to the critical inflexion point, after which the Luna economics turn positive.
As positive as this might be though, so long as local governments remain skeptical of cryptoassets, it is unlikely that this viral loop will be activated.
Demand for txs = value appreciation for Luna
By now, it should be clear that Terra has been architected in such a way, that makes demand for transactions the critical variable in its value model. So far, the team has implemented 1 stable pair - the Korean Won (KRW), with plans to expand in a multitude of currencies that include the USD and the IMF's SDR.
From a strategic standpoint, the decision to start with the KRW seems smart for a couple of reasons; (i) Korea is one of the most technologically advanced countries globally, with the 2nd highest % of Information and Communication Technology as a proportion of GDP, and 2nd highest % of R&D spend among OECD countries.
Not only does that improve the adoption potential for Terra, but also (ii) given the relatively insular nature of Korean currency markets (see: Kimchi premium), it provides for a "natural" incubator by protecting Terra from external competition. That allows Terra to iterate fast and capture market share in the Korean and ASEAN markets, leveraging local networks, while ironing out the model and improving its potential for further expansion.
Further, the team has explicitly targeted e-commerce as the first market they will be focusing on, a burgeoning industry that has been experiencing anywhere between 5% and 65% CAGR in the region, over recent years. One of Terra’s core strategies is to build an alliance of e-commerce sites and operate as a payment platform for them. The Terra stablecoin may also be offered as an incentive for those making purchases on these sites - a strategy that is serviceable due to the cost efficiency that Terra's blockchain back-end achieves.
In order to bolster their go-to-market capabilities, Terra launched CHAI, a consumer facing e-commerce application for everyday purchases (to illustrate, a large proportion of purchases are reportedly for rice) that works with Terra's blockchain as the back-end payment rails. According to reports from Terra, CHAI has seen 250k sign-ups since launching a few months ago, with $1.3M volume processed.
A quick look at the Terra block explorer points to an approximate equivalent $1.5k as the current daily transaction volume - a figure that pales in comparison to legacy internet native competitors. To illustrate, appox. $200M daily volume processed by Adyen, a Dutch competitor of Stripe that recently underwent an IPO at an $18B valuation. Be that as it may, in the short few months the platform has been live, volume has been growing linearly, showing a healthy - albeit pre-exponential - growth pattern.
While somewhat protected from global markets competitors, Terra faces strong domestic competition from Kakao/Klaytn (who has also a stake in Terra), Toss and other legacy payment solution providers.
Should one be a buyer of Luna at this point?
Terra has secured $32M from Polychain, Arrington XRP and Binance Labs - among others, in a sale that concluded in September 2018. Various ICO listing sites point to the ICO price per Luna token, standing at $0.80. Given the pre-sale patterns we have seen over the years, we could speculate that the price that early investors came in is closer to to $0.2. Anecdotal information we have collected, point to Luna tokens changing hands OTC pre-Mainnet for as much as $2.4 per Luna, which would have put early investors at over a 10x return at that point.
Currrently, the token is trading at $0.43, having listed at approx. $1.7 per token; that's a 75% drawdown, that puts the early investors in the 2x gain region - likely with more realised already, and less of an incentive to sell down on the remainder of their positions.
Arguably, one could pick a worse moment to start building a position, although the lack of liquidity might prove to be an issue, depending on the intended position size.
My take on Terra's valuation
To further put some context on current price levels, I went ahead and built a DCF model to value Terra. The premise is that a DCF model applies really well to valuing Luna tokens, as staking Luna is a claim to a stream of future cash flows (tx fees).
Model assumptions
I benchmarked the 3 industries that are most relevant to Terra (shown below), projected their growth in tx volumes according to 3rd party estimates over 10 years, estimated how much share blockchain based solutions are poised to capture over those 10 years (different S-curves) and made an assumption on the proportion of the blockchain quadrant Terra is likely to represent in each industry.
The main assumptions that govern the model beyond the ones mentioned above, are:
a 0.35% tx fee - adjusted downwards from the average {0.1% to 1%} to reflect the cost of running a validator
a 40% discount rate - industry standard for VC
an 80% main use case contribution level - assuming that most of the value transacted on Terra will come from the 3 industries benchmarked
a 25% staking rate - reflecting the current state of Luna staking / total supply
a 2% annual growth rate after the 10 years modelled to capture the terminal value
You can access the model and try your own assumptions here.
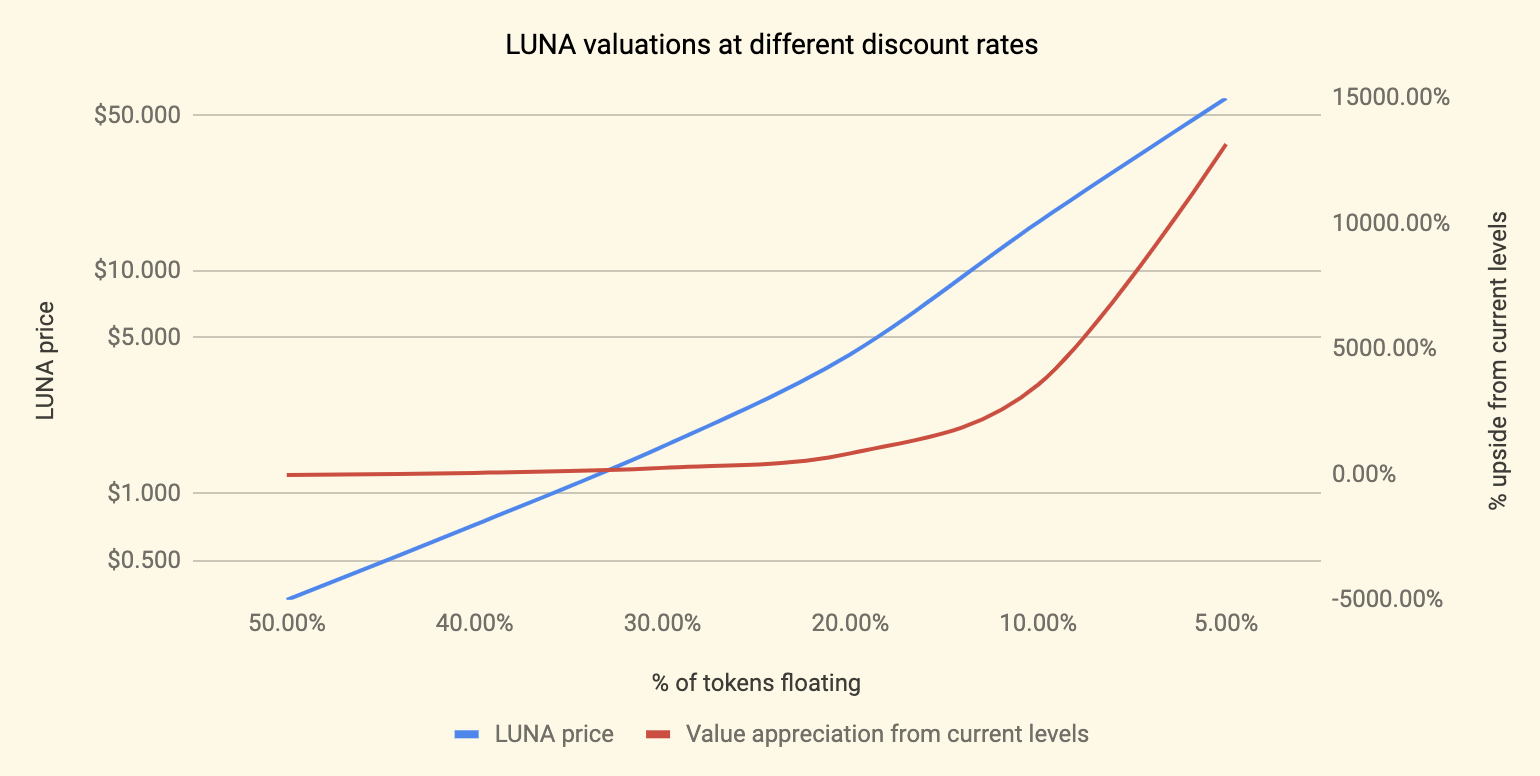
The result on the base case scenario, is an estimated $0.72 per Luna, at a $180M network valuation.
What is interesting about the result is that in a scenario building exercise (changing one of the key variables and keeping all else constant), the base case outcome sits a few standard deviations to the left of the mean, implying that at this point there is more upside to owning Luna than downside.
To illustrate, if we assume that 50% of the tx volume on Terra will come from other than the 3 main use cases, then the fair price per Luna token stands at ~$1.3 (3x from current value). If we further relax that assumption to 10%, then the projected upside stands at 10x. Equivalently, while exploring different discount rate levels (reflecting different levels of perceived risk), we find that a 50% discount rate yields a fair price of $0.33 per Luna (a 25% downside), while a 30% rate yields $1.62 per Luna (a 4x outcome) and so on.
What is rotten in the state of Denmark...?
There is a lot that's right about Terra; a great team, a straight-forward token model, a very technology-friendly home market, the potential for explosive growth in the coming years, an attractive current valuation and not many project specific risks. Regarding the latter, there are three main risk drivers that I see here - namely (i) the hidden negative multiplier - covered in an earlier section, (ii) the risk that price oracles introduce in the model, and (iii) the time-lags that exist in the stabilisation model.
As far as (ii) is concerned, this is a problem that underlies the whole blockchain industry and as such I am more inclined to bucket as a systemic type risk. There are currently many solutions being iterated upon, including some higher profile ones from Chainlink and Maker DAO, but also some newer ones like DIA.
Regarding (iii), this is something that I need to spend some more time thinking on. The risk here lies in that the supply side mechanisms that ensure the peg remains stable, will be slow to react to demand side fluctuations - or that the market won't pick them up soon enough. At the scale Terra is at now, the effect should be miniscule.
However, in a condition of large transaction volumes, this could lead to poor price discovery for Terra users and a lot of unintended costs creeping up on merchants' and users' balance sheets.
Parting thoughts
Doing some quick mental accounting on the case presented above, it is fairly clear that the upside here outweighs the downside. The combination of a great market, a great team, an appropriate price point and a novel configuration of blockchain technology in collapsing unit costs, make Terra/Luna an attractive opportunity. If there is ever someone to disrupt Paypal and Stripe, they are likely to look like this in the back-end.
Were one to hold Luna, the incentive is for them to have a long-ish hold horizon, while they would have to be prepared for the potential of further short term value depreciation. However, if there is fundamental belief in the team's ability to execute and the existence of a large enough market for Terra, then the risk is likely a risk worth taking.
And as always - this is a business case exploration and not financial advice. Be safe out there.
Beyond the hype on xDai
Aka, the DAI of DAI, the native Ethereum stablecoin for fast and cheap P2P transactions, and one of the more hyped projects to come out of the Ethereum developer ecosystem in 2019. By way of xDai recently raising a $500k round led by B-Tech - the investment arm of BitMax.io and Focus Labs - the project came to my attention recently and thought it would make for a good Daily exploration. So without further ado, I'll take some time to present you with the TL;DR on xDai, along with a few quick-fire thoughts on what's good and what's not about the project.
What is xDai?
xDAI is both an Ethereum sidechain, and a token that is pegged to the US Dollar via the DAI, has extremely low transaction fees, and very fast transaction times.
The project was brought to life in a collaboration between POA Network (one of the more active developer teams within Ethereum) and Maker DAO. Users can convert Dai to xDai via POA Network’s TokenBridge, which connects Ethereum and xDai chain.
How does xDai work?
The xDai blockchain is a wholly separate network from the Mainnet that achieves much higher throughput by scaling up the block size and scaling down the block producer (validator) count. The sidechain mechanism is powered by POA's Tokenbridge, and as such requires an own set of validators, separate to those active in Mainnet.
xDai works with 10 validators that are responsible for running nodes and setting the network parameters.
The way xDai is minted works as follows: you lock DAI in a contract on Mainnet, and the validators on the xDai chain mint DAI on the xDai chain to you. Effectively, xDai trades decentralization for performance.
Why xDai and not just DAI?
As a Mainnet token, the DAI is subject to the wild fluctuations that transaction costs on the Ethereum network undergo - tied to a large extent to the availability of resources on the network.
The chart below shows how the history of the median transaction fee on Ethereum, since Q3 2017. Indicatively the median tx fee for 2019 is close to $0.1.
Via the sidechain mechanism (and some sort of transaction batching/key-synching bridge with Mainnet) xDai manages to perform transactions at a steep discount to DAI on the Ethereum Mainnet. More specifically, the cost to perform a transaction on xDai, is about $0.000021.
As we explored above, more recently the same function in Ethereum costs 4000x more (or 0.25% of the transaction value on average), while in the normal financial world, with what it costs to send money in the normal the cost of money transfers is upwards 3% (for international transfers).
Similarly xDai records impressive performance in the transaction speed dimension too. Transactions on the xDAI blockchain occur within five (5) seconds, while a typical Ethereum transaction takes about 1–3 minutes and a normal financial world international transfer, way over 24 hours.
And what about early traction?
Established in October 2018, xDai Chain has attracted the attention of the ecosystem, thanks in no small part to Austin Griffith’s Burner Wallet, which provides a quick and easy way to carry and exchange small amounts of spending-crypto using a mobile browser and serves as a low-friction way to onboard new users.
xDai was used at ETHDenver (Feb 2019) as a platform for the Burner wallet, which allowed thousands of attendees to seamlessly buy food and transfer funds. 11 food trucks accepted xDai via Burner Wallets and sold 4,405 meals for a total of $38,432.56. And the total fees were only $0.20.
xDai was also used during ETH New York, though no similar figures have been made public. Beyond that, there is only one Dapp outside the wallet contingent that uses xDai - and that is the somewhat fringe prediction's market Helena.
Having reviewed what xDai is and how it works - brief as it might have been, let's now consider what xDai has going for it and where it falls short.
In favour of xDai...
- Ultra fast and cheap transactions with stable value. Could really be a game changer for Dapp adoption by providing a significant UX improvement.
- Can see it having significant impact in P2P payments (although one can argue that this is not really a problem in the developed world).
- Supported by two of the strongest developer groups in crypto (MakerDAO and POA).
Against xDai...
- Pegged to DAI, therefore pegged to USD, right? Wrong! The DAI is notorious for breaking its peg with the USD.
- If Ethereum eventually scales via Ethereum 2.0, then xDai is obsolete, as the DAI itself will enjoy similar transaction speed and cost.
- Clunky UX; like with many things in crypto, getting xDai as a user, is far from easy. A user journey would look like this: buy ETH on Coinbase (Pro) with USD, exchange ETH for DAI, transfer the DAI to the Dex Wallet mobile app (dl the app), and exchange DAI for xDAI. Far from ideal.
- Adoption story is over-sold; a quick glance at the types of transactions taking place on the xDAI chain, show virtually 0 P2P usage. Contract call type transactions are disproportionately high, while the most common USD amount transacted comes with 4 to 5 decimals.
- Centralized; 10 validators control the parameters of the ecosystem. This might not matter much as long as xDai is inconsequential, but will certainly matter if/as things progress (e.g. see EOS).
For all its promise, xDai seems to lose out in a tit for tat and leaves the observer with much more to be desired...